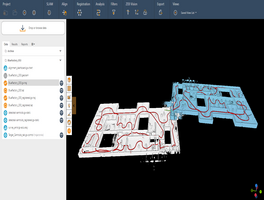
An image shows a map of the measured Gulf hypoxia zone, July 21-26, 2024 (top). The red area denotes 2 mg/L of oxygen or lower, the level considered hypoxic, at the bottom of the seafloor. A graph (bottom) shows the long-term measured size of the hypoxic zone (green bars) measured during the ship surveys since 1985, including the target goal established by the Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Watershed Nutrient Task Force and the 5-year average measured size (black dashed lines). (Credit: NOAA/LUMCON/LSU)
National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration (NOAA)-supported scientists announced that this year’s Gulf of Mexico “dead zone”—an area of low to no oxygen that can kill fish and marine life—is approximately 6,705 square miles, the 12th largest zone on record in 38 years of measurement. This figure equates to more than 4 million acres of habitat potentially unavailable to fish and bottom species, an area roughly the size of New Jersey.
Scientists at Louisiana State University and the Louisiana Universities Marine Consortium (LUMCON) led the annual dead zone survey July 21-26, 2024, aboard LUMCON research vessel Pelican. This annual measurement is a key metric that informs the collective efforts of the Mississippi River/Gulf of Mexico Hypoxia Task Force, a state/federal partnership which has set a long-term goal of reducing the 5-year average extent of the dead zone to fewer than 1,900 square miles by 2035.
While the NOAA-supported research surveys provide a one-time snapshot of the dead zone, the five-year average captures the dynamic and changing nature of the zone over time. The five-year average size of the dead zone is now 4,298 square miles, more than two times larger than the 2035 target.